Analysis of Synchronous belts failure
There are several possible causes of belt breakage or wear: friction, misalignment, unsuitable tension, unsuitable pulley teeth, etc.
FINDINGS
DIAGNOSTIC
TIPS
Excessive wear of the belt flanks
- Incorrect handling
- Flange damaged
- Belt too wide
- Not enough tension
- Rough flange
- Poor meshing
- Belt in contact with housing
- Follow installation instructions
- Repair the flange or replace the pulley/flange assembly
- Use an appropriate pulley
- Check tension and compare with recommended value
- Repair or replace the flange (avoid rough materials)
- Correct alignment
- Remove obstructions
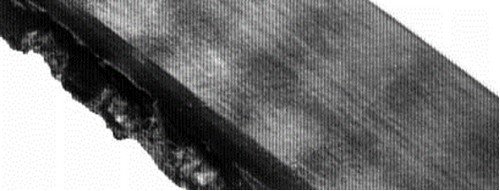
Breakage of traction ropes
- Excessive shock loads
- Insufficient pulley diameters
- Incorrect handling / storage
- Dirt or foreign object in transmission
- Eccentric toothed pulley
- Recalculate the transmission and adapt it to functional constraints
- Recalculate the transmission and use larger diameters
- Follow handling and storage recommendations
- Remove debris and check the housing
- Replace the pulley
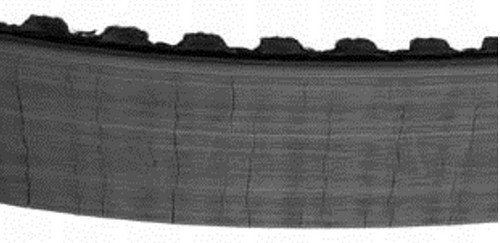
Cracks
- Insufficient pulley diameters
- Outer roller
- Extremely low starting temperatures
- Prolonged contact with harmful chemicals
- Poor hub/pulley assembly
- Recalculate the transmission and use suitable diameters
- Use an inner roller or increase the diameter of the outer roller
- Preheat the installation before starting
- Protect the transmission
- Fit the hub according to the instructions
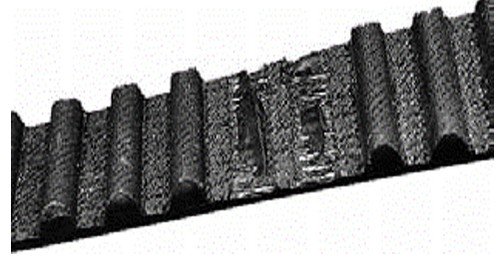
Premature wear of teeth
- Tension too low or too high
- Belt partially off pulley
- Misalignment
- Unsuitable Belt teeth (e.g. HTD®, GT, etc.)
- Worn pulleys
- Rough pulley teeth
- Damaged pulleys
- Pulleys of inadequate size
- Belt in contact with casing or supports
- Excessive load
- Pulley material not hard enough
- Dirt or foreign object in transmission
- Poor hub/pulley assembly
- Adjust to recommended value
- Correct the alignment of the non-flanged pulley
- Correct alignment
- Use correct Belt/Timing belt combination
- Replace pulleys
- Replace pulleys
- Replace pulleys
- Replace pulleys
- Remove obstructions or use a roller
- Recalculate the transmission and adapt it to the required loads
- Use pulleys of a different make
- Clean the transmission and check the housing
- Fit the hub according to the instructions
Pulling teeth
- Excessive jerking
- Less than 6 teeth in mesh
- Eccentric pulley
- Pulley wear
- Outer roller
- Unsuitable Belt teeth (e.g. HTD®, GT, etc.)
- Misalignment
- Insufficient tension
- Recalculate the transmission and adapt it to the required loads
- Recalculate the transmission
- Replace the pulley
- Replace the pulleys
- Use an internal roller
- Use correct belt/pulley combination
- Correct alignment
- Tension the Belt according to the recommended values